Risk management systems allow computer information to collect risk data and eliminate business risks. It’s used to ensure that the bank’s internal controls meet the requirements of regulatory agencies. An example of this would be the Basel II accords. These standards were created to help banks understand what they need to do to reduce their exposure to potential losses from loan defaults. One of the first aspects to have a well-rounded understanding of the concept is to identify the differences between integrated risk management vs enterprise risk management.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a systematic approach to identifying, measuring, analyzing, controlling, monitoring, reporting, and mitigating risks associated with the organization’s operations, strategies, and assets. It is often referred to as “risk-based management.” ERM can include both quantitative and qualitative approaches.
Integrated risk management (IRM) is the application of different types of risk management techniques that are used together to reduce overall risk. This can include multiple forms of risk analysis, forecasting, scenario planning, stakeholder engagement, etc. This is one of the most useful types of risk management in banking and other related industries.
Here is a list of risk management standards to look out for:
Internal Control Systems
Internal control systems are designed to provide assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting information. They are typically implemented at the entity level and are focused on ensuring that the accounting records and reports are reliable and that transactions are properly recorded per the adopted security measures put in place.
Operational Risk Management System
Operational risk management systems focus on identifying and measuring operational risk exposures and minimizing those exposures through effective monitoring, mitigation, and control processes. This type of risk management focuses on the day-to-day operation of the business. Activities like employee error, natural disasters, business processes, and automation breakdowns are all examples of operational risk.
Compliance Management System
Compliance management systems (CMS) are intended to assist organizations in meeting legal, ethical, regulatory, and other security compliance requirements. Compliance managers may use various tools to assess the effectiveness of existing policies and procedures, develop new ones, and implement them across the organization. Implementing a CMS includes keeping up on responsibilities like:
- Risk monitoring
- Regularly updated employee awareness training
- Provide departments with resources needed to take necessary corrective actions
- Protect consumers in the event of an attack
Risk Management in Banking
Operational risk refers to any potential loss that might occur due to human error, fraud, or other factors related to the operation of the business. This includes legal issues, employee misconduct, theft, environmental damage, natural disasters, etc. The goal of operational risk management is to reduce losses from these events and increase the probability of success.
It is crucial for banks to have an integrated cybersecurity and risk management strategy to combat the evolving cyber threat landscape. An integrated strategy will help ensure compliance regulations are met, protect brand integrity, improve shareholder confidence, and stay up to date on risk management best practices.
When dealing with large amounts of money, banks need to manage credit risks effectively to protect their assets and the assets of their customers. Banks use different methods to mitigate risk, including lending limits, rating agencies, and collateral requirements.
Questions?
We can help! Talk to the Trava Team and see how we can assist you with your cybersecurity needs.
What is a Risk Management Information System?
Risk Management Information System (RMIS) refers to the systems that are used by organizations to identify, assess, monitor, control, and reduce business risks. An RMIS helps organizations to manage their risks better and make informed decisions. So, what is risk management information system used for? Risk management is the systematic approach to identifying, assessing, monitoring, controlling, and reducing business risks.
The following are some of the advantages of risk management information system:
- Identifies and analyzes risks at an early stage
- Provides a basis for making informed decisions
- Helps to improve organizational performance
- Improves internal controls
There are different types of risks in information systems to look out for. Below are some of the most important types of risks to your organization:
Information risk
Information risk refers to the risk that arises from the use of information systems. This type of risk can take place in many different ways, including through the misuse of data, the loss of data, unauthorized access to data, etc. Therefore, this type of risk can be classified into two categories: operational risk and security risk. Information risk management helps protect organizational assets, individual employee assets, and partnered organizations. When information is shared between organizations, security strategies need to account for breaches within both organizations.
Security Risk
Security risk is about threats posed by people who want to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information stored in computers or other electronic devices. Security risk can be divided into three types: physical, administrative, and technical. Physical security risk involves the possibility of theft, damage, or destruction of assets. Administrative security risk includes attacks aimed at gaining control over systems and networks. Finally, a technical security risk is the threat of malicious code being introduced into a system.
Risk Management Process
Some people will ask security professionals, “What are the five steps in risk management process?” In our experience, the risk management process is actually better defined by 6 steps. Here are the 6 steps of risk management process.
Hazard Identification
First, it’s crucial to begin the process by inspecting areas that could have potentially caused harm. Ask your co-workers if there are any negative changes they have noticed. They may have been aware of something risky that didn’t catch your attention at first. Check manufacturers’ instructions or data sheets for chemicals and equipment, as they might have information that can help you identify the type of risk that has occurred. Lastly, take a look at past risk records. These often help to identify hazards that have been dealt with before.
Identify the risk.
Risk identification is the first step in risk assessment. This is done by identifying potential risks that may occur and analyzing them to determine if they are likely to happen.
Assess the risk.
Assessing the risk involves researching the details of the risk closely. Once classifying the type of risk, start taking note of factors that this type of risk includes. It can include criteria such as the severity level of the risk and the likelihood of it happening again in the future.
Controlling the risk.
Once identifying and assessment have been classified, it’s important to begin planning a process to eliminate the hazard. This stage involves testing different solutions and figuring out what controls the risk best. It’s often recommended to plan out control plans when situations like this occur. Overall, the focus should be on finding a solid solution to replacing the danger of the hazard.
Documenting the risk
Keeping records of risks is important because it helps identify risks that could re-occur. It helps track familiar factors of the hazard to understand how to deal with eliminating it. Documentation should include information such as types of hazards identified, association with other types of risks, IT risk assessment templates, dates of when the hazard was first noticed, dates of when the solution to the risk was implemented, the effectiveness of the control strategy for the risk, and any other relevant information about the hazard.
Monitoring and Reviewing
Even after finding a solution, it’s important to check back frequently to make sure that the solution for the risk is maintained properly. Factors like the environment and substance around the system play a huge role in either benefitting or destroying the risk solution. When not monitored correctly, new hazards could be introduced from existing hazards, causing more issues to a system. Risk Management Systems are ongoing processes that must be handled with proper care.
Following the risk management process steps above will help ensure your organization is handling risk adequately and sticking to compliance regulations.
Do you know your Cyber Risk Score?
You can’t protect yourself from risks you don’t know about. Enter your website and receive a completely free risk assessment score along with helpful information delivered instantly to your inbox.
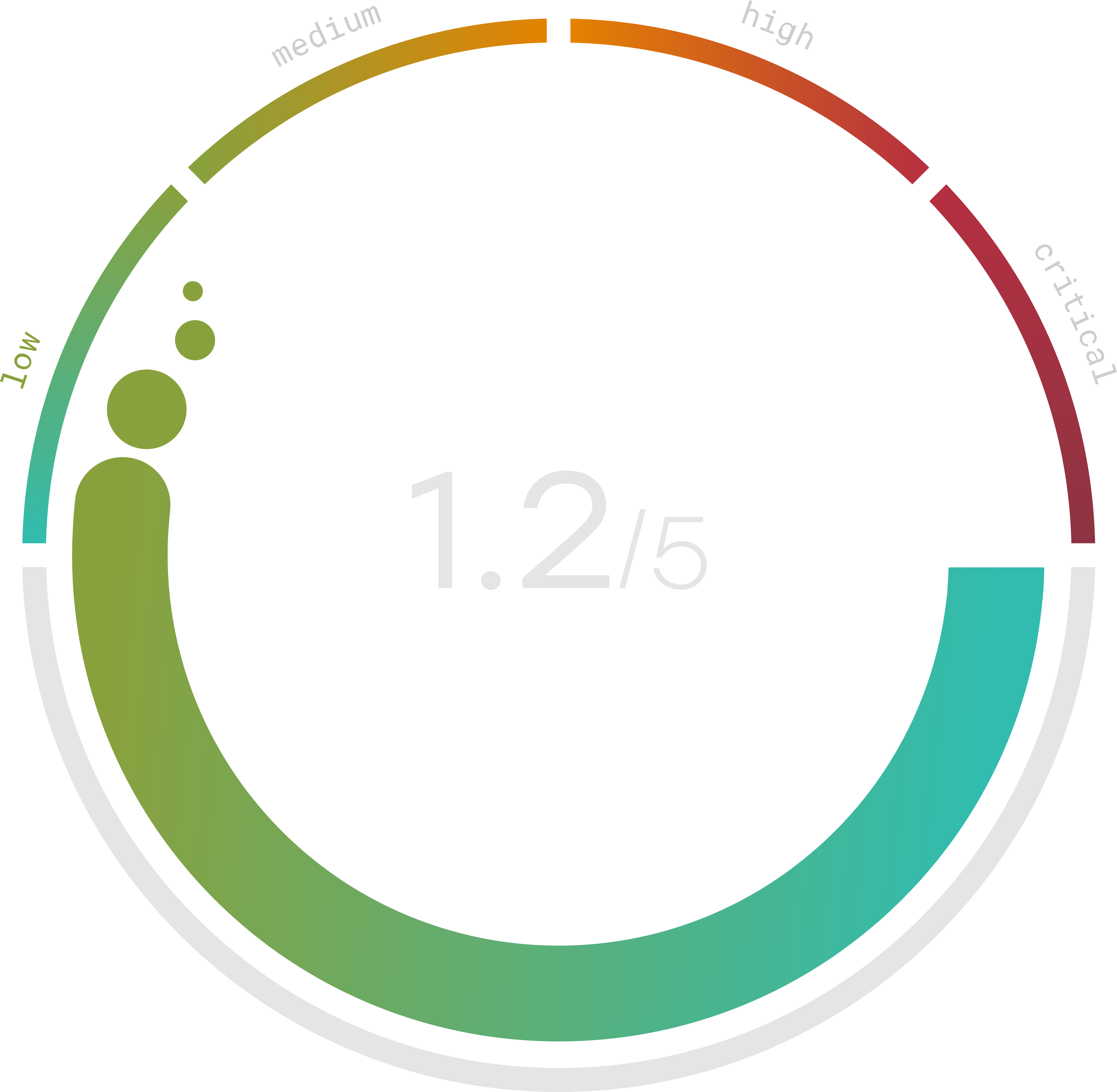
Risk Management System Examples
An effective risk management system is defining what constitutes a risk. Some common types of risks include legal, financial, reputational, operational, environmental, security, and human health. Once you have identified the type(s) of risks you are dealing with, you need to determine whether the risk is internal or external, and how severe it might be. Even though you want to trust your employees, 36% of breaches are caused by malicious internal actors.
You may then want to consider whether the risk exists at any stage of your business operation cycle, including from inception through production, distribution, and post-sale services. For example, the risk management process in project management is crucial to ensure you are maintaining the reputation your brand has worked hard to build and preparing your team for any potential risks the project may encounter. For an information security risk assessment example, visit Trava Security. Finally, you should look at ways to quantify the impact of the risk. This information can help you prioritize your efforts and allocate resources effectively.
Once you have determined the risks associated with your business, you need to decide where to focus your attention. In many cases, you can eliminate certain risks simply by avoiding them. However, if you cannot avoid a particular risk, you should still try to minimize its effects. Especially for a risk management system in banks, one way to do this is by implementing preventive measures. These measures may involve changes to policies, procedures, and practices, or improvements to existing systems and processes. If these preventative measures fail, you can use other methods to address the issue, such as training employees, improving communication, and providing additional resources.
Integrated Risk Management Vs GRC
People often ask, “What is integrated risk management?” In reality, this term can be used to describe a broad range of approaches that are designed to address risks across different business functions. The integrated risk management framework identifies, measures, monitors, and reports. Governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) are the integrated factors that address and improve objectives. According to OCEG, a well built integrated risk management example is one that excels in creating an approach that ensures the right people get the right information at the right times. The difference between the two is that GRC includes an organization’s strategies alongside risk management. Integrated risk management focuses on managing governance risks to the organization.
Trava provides a comprehensive suite of solutions for managing risks related to your company’s physical assets. Our solutions enable organizations to achieve compliance while reducing costs and improving cybersecurity strength. To keep your customer’s trust. They trust your company with the data they share. Trava Security uses its risk management system to help your company strategically. Consider signing up for a free cyber risk checkup today.
