In the current highly digitized landscape, one lingering challenge is that managing cybersecurity risk across enterprises is more complex than ever before. Even the most skilled IT teams admit that it is overwhelming to keep architectures and systems secure and compliant, given the internet of things (IoT) expansion. The reality of our interconnected world means that vast amounts of data are collected, transmitted, and stored within an organization’s system. Data is an essential and valuable tool for organizations. Unfortunately, as is often the case, the risk for an item of value increases at an equal or even higher rate than that of the item’s expansion. This ushers in great responsibility to mitigate any threats and risks to information and prevent exploitation from bad actors.
Organizations that want to balance the value of new technology against the cyber risk it carries will need to invest in awareness and preparation. To successfully manage risks, organizations need first to build knowledge of the risk management process, identify the critical action steps and then understand the essential capabilities they will need to conduct assessments and manage risk effectively.
The Current State of Cybersecurity
Understanding the current outlook of cybersecurity provides insights on how to protect your organization and mitigate exposure before a cyber event. Cybercrime is continuously growing; understanding this will help you develop an evolving cybersecurity strategy. According to the Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2023 report from the World Economic Forum, geopolitical instability is intensifying the risk of catastrophic cyber-attacks. Also, organizations face a growing number of laws and regulations. These dictate how confidential data must be protected, putting more pressure on IT teams and organization resources.
Organizations can now take on cyber risk insurance to hedge against the potentially devastating effects of cyber threats. This includes ransomware, malware, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS). However, this is still a relatively new concept. The policies available change from time to time, given the dynamic nature of the associated cyber risks. In addition, underwriters of cybersecurity insurance policies have limited data to articulate risk models. This makes it challenging to determine rates and premiums.
LISTEN IN TO LEARN MORE FROM MJ INSURANCE AND TRAVA DURING A JOINT WEBINAR.
Critical Cybersecurity Risk Terms to Know
Effective cyber risk mitigation requires you to understand the different terminologies used and the consequences of their convergence. There exists a lot of confusion and misuse over specific cybersecurity terminologies. They include:
Threats
Threats are situations or events with the potential to cause harm or disruption to an organization’s operations or assets. This is through unauthorized access, destruction, disclosure, or modification of information systems. They exist everywhere and in different forms and only become a problem when there is a vulnerability in your systems. For example, cyber threats can be hostile attacks, structural or configuration failures, human errors, etc.
Vulnerabilities
These are weaknesses or flaws within a security system that bad actors can leverage to fulfill a threat and compromise your network. Vulnerabilities of any size can cause data leaks and breaches, which can devastate your business. In addition, vulnerabilities in information security include network vulnerabilities, operating system vulnerabilities, process or procedural vulnerabilities, and human vulnerabilities.
Cyber risks
Risks are the adverse results that arise when threats exploit vulnerabilities. For example, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines cyber risk as the financial loss, operational disruption, or damage that occurs when your organization’s information systems fail or are disrupted by unauthorized use or access.
Controls
Controls are the structures or procedures put in place to prevent, detect and mitigate cyber threats. They range from physical controls, such as the use of surveillance cameras, to technical controls, like the use of firewalls and multi-factor authentication.
The Cyber Risk Management Process
Cybersecurity risk management is an ongoing process not restricted to the IT security team. Everyone in an organization has a role in ensuring a holistic perspective necessary for addressing risk comprehensively and consistently. Organizations must leverage the people, processes, and technology within their grasp to ensure security and privacy. This is to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data they are responsible for.
The core functions critical to a successful cybersecurity risk management process include: identifying, protecting, detecting, responding, and recovering. These functions serve as the backbone of the framework that other elements can be organized and built around. They facilitate a holistic cybersecurity program that helps organizations easily express their management of cybersecurity risk at a high level and informs risk management decisions.
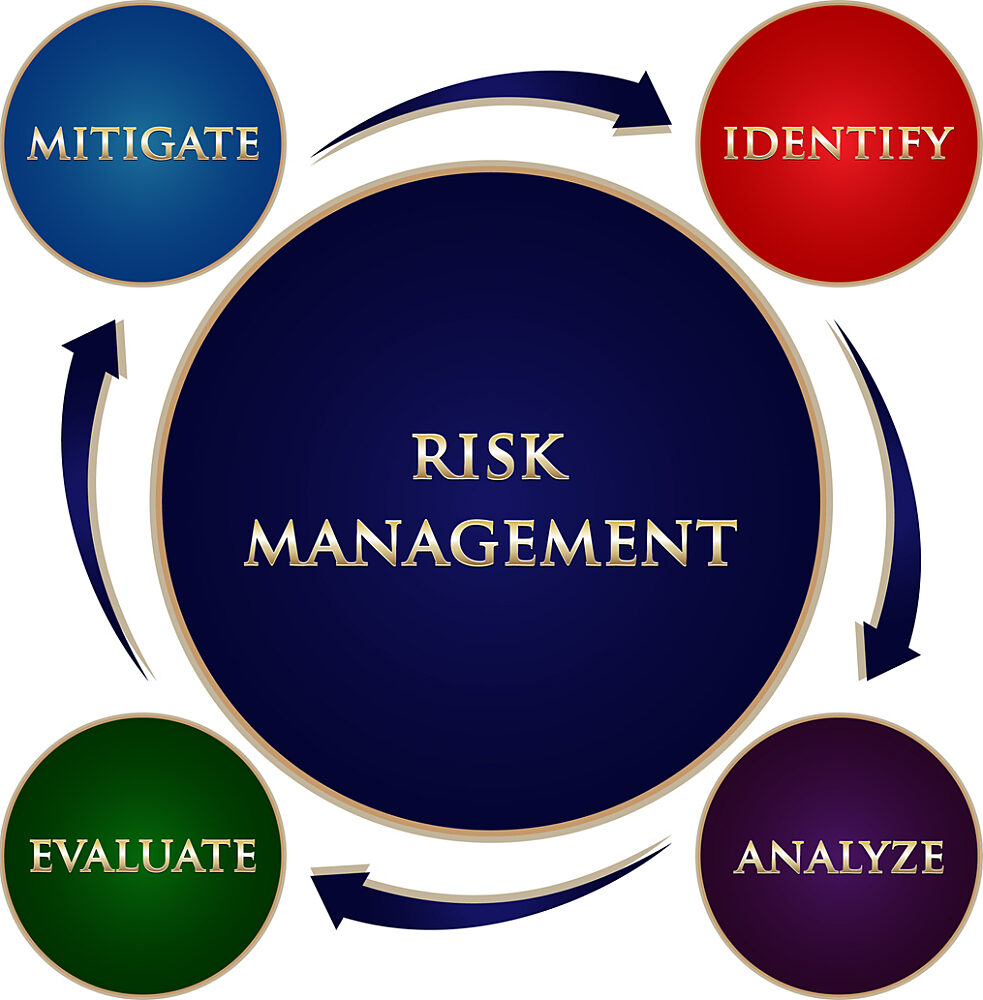
Identify
In this stage, organizations need to take steps to catalog and understand the systems, assets, and the people who comprise and influence their network and its security. This also means looking at the context of your business, players, and the necessary resources to maintain business continuity. For example, this may involve identifying physical and software assets, cybersecurity policies, and vulnerabilities within a system.
Protection or Preparation
It is much better to prevent cybersecurity incidents than waiting to learn the hard way how much disruption or damage they can cause to your business. It would be best if you had a strategy in advance. This is to reduce the risk of significant exposure. The protection or preparation phase outlines the procedures you have in place to minimize the detrimental impact of a breach. Examples of activities at this stage include training staff on cybersecurity, implementing access controls, and protecting resources and assets through maintenance.
Detect
There needs to be more than a strong defense against threats; your organization also needs to be well-prepared to discover breaches and other security events promptly. It would help if you operated under the assumption that a breach is inevitable since cyber threats are growing to be sophisticated by the day. You will need to implement continuous monitoring and evaluate your awareness. This is to ensure your team can quickly flag unusual activity and take action.
Respond
After detection, now it’s time to respond. Detection is like diagnostic and testing that helps us discover exactly what’s wrong and how we should respond. The actions you take at this stage reveal your ability to contain and mitigate the impact of a breach. This may include communicating with stakeholders and other relevant parties on the state of the breach, performing steps to prevent the spread of the breach ,and learning from the incident to avoid a repeat of the same.
Recover
This is the final stage in the cyber risk management process, where you can restore the full functionality of your systems following a cyber-security event. During the recovery stage, your organization needs to apply lessons learned from the incident to enhance response in the future.
Trava offers modern tools to help organizations run secure systems and productive businesses without fear of interruption or loss caused by cyber incidents. In addition, they bridge the gap between where you are and where you hope to be by helping you assess risk, seal off vulnerabilities, and transfer risk through insurance.
TRAVA ON. ANXIETY OFF.
We’re your partners in achieving whatever’s next. We just happen to use cyber to help you get there. Schedule a demo today!


