Last updated: January 7, 2026
Table of Contents
- Words Matters, Particularly in Cybersecurity
- Risk Vs. Threat Vs. Vulnerability
- What are threats?
- What is vulnerability?
- What’s Included in a Vulnerability Assessment?
- How to fix cybersecurity loopholes
- What does risk mean?
- How Do You Identify Threats and Risks?
- How to manage your cybersecurity risk
- What Is a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?
- How AI Is Changing Risks and Threats
- Cybersecurity Doesn’t Have to Be Complicated
- Why This Matters to Your Business
- A Reliable Cybersecurity Partner is Ready to Help
Threats, vulnerabilities, and risks can damage your business, your data, and your reputation, costing you millions of dollars and requiring extensive clean-up work. By understanding these security issues and taking action to prevent data breaches, cyberattacks, and phishing attempts, you can protect your business interests. The good news is that there are many tools now available to halt threats, vulnerabilities, and risks and to avoid potential security breaches, data corruption, system instability, and financial loss.
Companies across the globe are reevaluating their cybersecurity postures and implementing decisive approaches with a focus on cybersecurity and compliance. But while the specific strategies vary from business to business, enhancing network security begins with understanding safety and security terminologies.
Key Takeaways
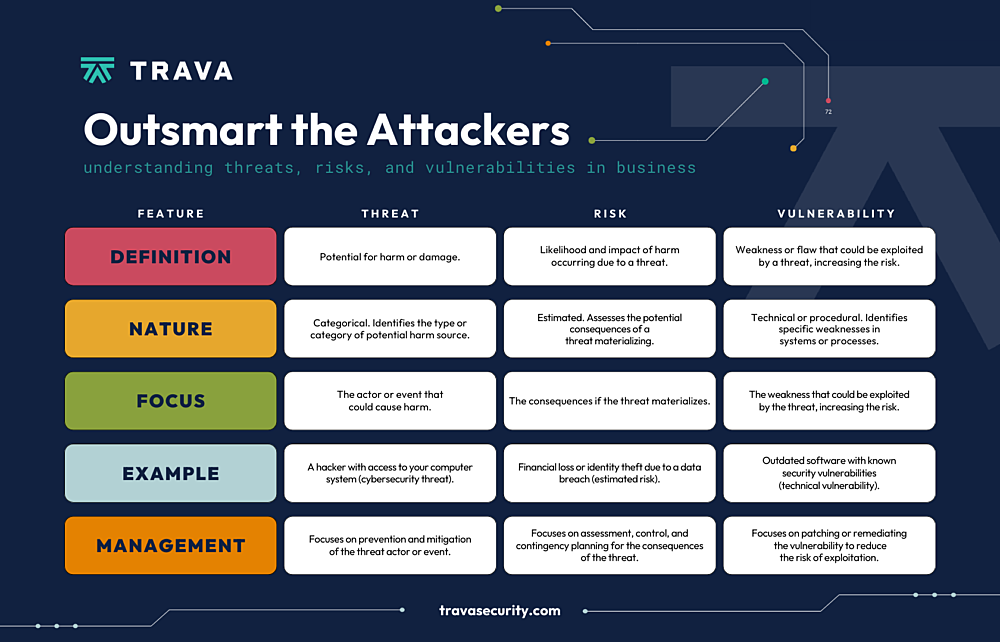
- A threat magnifies the chances of an adverse event, and a vulnerability is a weakness in your applications, networks, or infrastructure that exposes your data and assets to threats. A risk is the sum of a threat and a vulnerability — the potential for destruction, damage, or loss of data or assets.
- Your business can take advantage of a variety of cybersecurity risk assessment tools and services to enhance security and compliance throughout your organization. These tools allow owners and employees to recognize and prevent cybersecurity threats with appropriate training.
- Vulnerability assessments and cybersecurity assessments are proactive ways to detect threats before they damage your business. Conducting them annually, at a minimum, can bolster your security posture.
- AI is changing the global cybersecurity landscape. It can help your organization suss out bad actors and prevent security threats from taking root, though it must be used responsibly.
- Trava Security can help your organization develop an effective cybersecurity risk management strategy to safeguard your business and your assets.
Words Matter, Particularly in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity, like any other sector, has its unique lingo. What sets security jargon apart is how precise experts use niche terminologies and phrases within their language. But these terms may seem interchangeable to novices or lay people, who often blend them.
And since cybersecurity comprises multiple moving parts, anyone inexperienced with vulnerability management can easily get them mixed up.
Arguably, “threat,” “vulnerability,” and “risk” are among the most commonly confused terminologies. But unfortunately, twisting these words limits your grasp of today’s cybersecurity management technologies and tools. It can also hamper communication with other professionals on relevant topics.
Fortunately, the next section will guide you.
Risk Vs. Threat Vs. Vulnerability
So what do “threat,” “vulnerability,” and “risk” entail?
In essence, risk refers to the potential for destruction, damage, or loss of data or assets, resulting from a cyber-threat. On the other hand, a threat is what magnifies the chances of an adverse event, like a threat actor exploiting a vulnerability inside your system.
Finally, a vulnerability is simply a weakness in your applications, networks, or infrastructure that exposes your data and assets to threats.
Let’s review each of these terms in detail.
What are threats?
If you’re trying to protect an asset, then you’ll be shielding it from a threat. The term refers to anything that can accidentally or intentionally exploit a vulnerability and damage, destroy, or obtain an asset.
Online, your company website and data are the assets. A hacker and their tools (like malicious code) would be a cyber threat. The criminal can install the code on your site, which can infiltrate your platform and shut it down or install viruses.
The main types of cyber threats are intentional, unintentional, or natural.
- Intentional threats: Things like malware, ransomware, phishing, malicious code, and wrongfully accessing user login credentials are all examples of intentional threats. They are activities or methods bad actors use to compromise a security or software system.
- Unintentional threats: Unintentional threats are often attributed to human error. For example, let’s say you forgot to lock the back door before leaving for work. While you’re at the office, a thief seizes the opportunity to sneak into your home and steal your valuables. Even though you didn’t mean to leave the door unlocked, the thief took advantage of your home’s vulnerability. In the cybersecurity industry, someone might leave the door to the IT servers unlocked or leave sensitive information unmonitored. An employee could forget to update their firewall or anti-virus software. Current and even former employees may also have unnecessary access to sensitive data, or simply be unaware of the threats. (Which is why employee training is so important.)
- Natural threats: While acts of nature (floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, earthquakes, etc.) aren’t typically associated with cybersecurity, they are unpredictable and have the potential to damage your assets.
HOW TO STAY AHEAD OF CYBERSECURITY THREATS
Awareness is the best way to prepare for threats. You must stay current on data breaches, cyberattacks, and the methods hackers use to accomplish them. The most common hazards include malware, MitM (man-in-the-middle), DDoS (distributed denial-of-service), SQL injection, and phishing.
To protect yourself from cyber threats, continuously monitor all data environments and use two-factor authentication. You should also teach your employees how to recognize phishing attempts and other tactics cyber criminals use to trick people into helping them gain access to sensitive data.
What is vulnerability?
Vulnerability refers to a weakness in your hardware, software, or procedures. It’s a gap through which a bad actor can gain access to your assets. In other words, threats exploit vulnerabilities.
Take Kaseya. The FBI described the incident as “a vulnerability in Kaseya VSA software against multiple managed service providers (MSPs) and their customers.” Huntress, a cybersecurity firm, tracked 30 MSPs involved in the breach and concluded that the attack was due to an authentication bypass vulnerability in Kaseya’s VSA web interface. It allowed attackers to work around authentication controls and upload malware.
You should know that small to medium-sized businesses tend to be more vulnerable to attacks. That’s because few can afford a dedicated IT/security department, making it less likely that there are security procedures in place. (That said, cyber attacks affect companies of all sizes.) Companies should be aware of their threats and vulnerabilities in order to identify and respond to all of the risks. To determine the best way to approach a specific threat, perform regular threat assessments. Or try penetration testing, which recreates real-world threats to discover vulnerabilities.
What’s Included in a Vulnerability Assessment?
A vulnerability assessment from Trava can pinpoint weaknesses before cyber criminals take advantage of them. By recognizing and addressing weaknesses before they can be exploited, vulnerability assessment services can help safeguard your business’s systems, data, team members, customers, and reputation.
Conducting a vulnerability assessment at least once a year can include the following:
- Comprehensive scanning: Advanced scanning tools and techniques assess your entire IT environment, including your organization’s networks, applications, servers, and endpoints to locate weaknesses.
- Expert analysis and reporting: Vulnerability assessment services also incorporate analysis of the scan so you can prioritize areas of weakness based on their level of risk to your business.
- Remediation guidance: This step-by-step component focuses on strengthening your business’s defenses to protect your organization against future threats. We will review these steps with you and help you implement stronger security safeguards.
- Continuous improvement: We also provide ongoing support and recommendations to help you maintain a strong security posture and adapt to new threats as they arise. The ultimate goal is to continuously improve your organization’s security defenses.
Being proactive before danger strikes is critical to safeguarding your business today and into the future.
A key component of vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, also known as pen tests, are simulated cyberattacks that review your business’s digital infrastructure and identify potential vulnerabilities, making them a great tool to have in your security toolbox.
When you are better aware of potential cyber threats to your business, you can take steps to prevent them. With that in mind, a comprehensive vulnerability assessment will make it easier to prioritize risks so you can focus on the most serious issues first, improve your security posture by identifying unauthorized devices, and help your business meet regulatory requirements by addressing security gaps.
How to fix cybersecurity loopholes.
Proactive vulnerability management is the key to sealing website susceptibilities. Therefore, you should consider vulnerability management software for regular scans and assessments. Moreover, you must align your cybersecurity policy with ISO 27001 standards, implement strict access control, and create a robust contingency plan.
What does risk mean?
This is where vulnerabilities and threats intersect. At its core, risk refers to the possible implication of the damage or loss of business assets and data.
While it’s impossible to eliminate risk in its entirety, you can manage it to a level that aligns with your company’s tolerance. So don’t aim to achieve a risk-free system, but one with the lowest risk possible.
Notably, cyber risk is a function of threats leveraging system vulnerabilities to access and compromise or steal assets. It’s best summed up with this formula:
Risk = Threat + Vulnerability
Understanding these distinct concepts can help you determine your website’s overall safety. Of course, like cyber criminals, threats exist. But you’ll have the lowest risk when you don’t have vulnerabilities.
How Do You Identify Threats and Risks?
Your first step toward properly responding to a threat or mitigating a risk is to identify it. But this is easier said than done when security risks and threats often seem like nothing more than a misconfigured setting or an annoying email.
The difference between threat vulnerability and risk in cyber security is that while risks are a passive danger, threats are an active one. That means you can only identify a threat once an attacker targets your organization.
But that doesn’t mean your only option is to wait until it’s too late. There are many early warning signs that you should keep an eye out for:
- Repeat login attempts: An unusually high number of failed login attempts on company accounts is a sign someone’s trying to force their way past your password.
- Unexplained activity: Large amounts of data being transferred around or outside the network without prior authorization can be a sign of an insider threat.
- Suspicious email requests: A high frequency of inauthentic emails requesting confidential information from employees is known as a phishing scheme. Phishing is usually used as an “avenue of attack” rather than the end goal.
Meanwhile, detecting security risks requires continuous active monitoring, testing, and assessments of your infrastructure. Automation is a great help for network scanning, as manual check-ups can be incredibly time-consuming.
How to manage your cybersecurity risk
Considering the impossibility of eliminating cyber threats, risk management can be the most effective approach to enhancing your cybersecurity posture. This is an ongoing routine practice where experts review your risk environment to minimize the likelihood of specific threats.
What Is a Cybersecurity Risk Assessment?
Cybersecurity risk assessment services help your business identify and prioritize high-risk issues to secure your data and your reputation. The experienced cybersecurity risk assessment team at Trava Security provides trusted insights to pinpoint system vulnerabilities, securing them against cyber threats.
Your cybersecurity risk assessment report will include the following components:
- Review of your goals and expectations: We help you define the overall scope and goals of your assessment using a cybersecurity risk assessment questionnaire. This will give you the information and resources you need to confidently take the next step.
- Pre-assessment activities: At this stage, we pull together key insights on your IT infrastructure, security policies, and processes to support a comprehensive evaluation. We will review these with you to make sure that we are covering the key issues that could impact your particular business and industry.
- Risk assessment: We also include a comprehensive evaluation of your existing security controls, identifying potential threats and providing actionable recommendations for risk mitigation and prevention. This risk assessment will highlight areas of concern as well as opportunities for addressing them.
- Clear reporting: A thorough cybersecurity risk assessment report covers issues as well as recommendations for security enhancements for your business in language you can understand. We include the opportunities to discuss issues, strategize fixes, and answer all of your questions so you know how we’re protecting your information.
Your cybersecurity risk assessment will identify the potential consequences of a cyberattack and help you create a risk management plan tailored to your business. Then we will work on crafting a strategy that helps you manage risk for short- and long-term scenarios. Like vulnerability assessments, your business should perform a risk assessment once a year at a minimum to root out cybersecurity risks. Making them a key part of your strategic planning process is the ideal approach to maintain compliance and safeguard your assets.
How AI Is Changing Risks and Threats
Artificial intelligence (AI) is dramatically reshaping global risks and threats for businesses of all sizes by creating more sophisticated cyber threats, such as deepfakes and personalized phishing. Between March 2024 and February 2025, the cost of the average data breach in the healthcare industry reached a whopping $7.42 million, followed by the financial services sector at $5.56 million per breach.
AI is also helping organizations advance their defenses, detect threats faster, and support rapid responses to potential issues. While AI attacks can break out in less than an hour, response times are faster than ever. AI can analyze massive amounts of data in a short time to identify potential issues such as unusual logins and suspicious network activity.
Some AI-powered security solutions include the following:
- Cisco Stealthwatch: This vigilant system engages advanced machine learning algorithms to continuously monitor your network traffic, quickly flagging any irregularities or potential threats in real-time.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: Your business’s all-in-one security powerhouse, Cortex XDR combines network, endpoint, and cloud security with AI-driven analytics to uncover and thwart advanced threats.
- IBM QRadar: This security information and event management (SIEM) system integrates artificial intelligence to analyze log data, network flows, and user behavior. It seeks out any unusual activity and notifies you immediately of potential issues.
- Splunk Enterprise Security: This solution brings together machine learning and analytics to spot security threats and offer real-time visibility into security events. It’s designed to help your business stay one step ahead of cyber criminals.
- Darktrace Enterprise Immune System: Learning the normal behavior of your network, Darktrace Enterprise Immune System can swiftly detect any deviations from the baseline. From insider threats to sophisticated attacks, this AI system serves as real-time protection for your business.
While AI requires robust governance to prevent misuse and bias, it can also serve as your right-hand companion for protecting your company’s digital assets and data. Artificial intelligence today can offer real security support for your business that prevents threats from happening and keeps your business running smoothly. The use of AI can also support your cybersecurity budget.
We can help you use AI to support your business’s cybersecurity goals. Trava also offers customized cybersecurity due diligence for private equity and venture capital and other businesses and industries that require the highest security services.
Cybersecurity Doesn’t Have to Be Complicated
A robust security strategy is your only way of navigating the treacherous cybersecurity landscape. Organizations must heed the above recommendations to ward off threats, seal vulnerabilities, and reduce cyber risks.
But creating an effective plan that can seal all the loopholes and fight back threat actors is easier said and done.
A comprehensive program requires lots of resources and effort. But however daunting it may seem, the legal, financial, and reputational implications of cyberattacks outweigh these costs by far. Thus, you cannot afford to compromise.
Savvy organizations, especially SMEs, are overcoming the hurdles by partnering with reputable cybersecurity experts instead of relying on on-premise solutions. This can be a valuable decision, as it can help you:
- Boost your security cost-effectively
- Gain insights from industry experts
- Monitor your systems in real-time and conduct instant analysis
- Save time to focus on core business
- Leverage a proactive approach that focuses on prevention than cure
- Heed cybersecurity standards and compliance requirements
You’re on the right site if you’re looking for all these.
Why This Matters to Your Business
You can probably see why it is so important for your business to understand threats, risks, and vulnerabilities and to proactively work to prevent them before they negatively impact your organization or your data.
If you’re still not convinced, consider the following chilling statistics:
- In the second quarter of 2025 alone, nearly 94 million data records were leaked in data breaches, impacting millions of individuals across the globe.
- Your customers care about cybersecurity. Sixty-six percent of consumers don’t trust companies that suffer from data breaches and 75% say they would stop shopping with a brand that has been the victim of a notable security incident.
- And the potential financial losses are significant. Cybercrime costs across the globe are expected to reach $10.5 trillion this year alone.
Businesses today also tangle with data corruption and system instability due to cyberattacks. Simply put, all of this definitely matters to your business and to your customers.
A Reliable Cybersecurity Partner Is Ready to Help
The experienced team at Trava understands that you need unique solutions to your cybersecurity needs. Our experts can meet you where you are and help your company minimize threats, fix system vulnerabilities, and transfer risk through insurance.
So don’t hesitate to contact us.


